Discover how Functional Testing Power builds user trust, prevents defects, and ensures dependable digital experiences across applications, APIs, and distributed systems.

Introduction: Code Meets Confidence
In the vast digital landscape, Functional Testing Power plays the role of invisible guardian. Every line of code is intention — and functional testing ensures that intention becomes predictable, reliable execution.
Whether it’s a fintech transaction, a healthcare workflow, or a global-scale SaaS product, functional testing verifies one critical truth:
-
Introduction: Code Meets Confidence
-
Functional Testing for Software Integrity: The Architecture of Assurance
-
The Core Anatomy of Software Integrity
-
Functional Testing as Craftsmanship
-
Functional Testing for Software Integrity in Distributed Systems
-
Microservices, APIs & Modular Functional Testing
-
The Power of Test-Driven Development
-
Automation: Scaling Functional Testing for Software Integrity
-
Quality-First Culture in Modern QA
-
Compliance & Trust: Functional Testing as Ethical Assurance
-
Conclusion
-
Internal Links
-
External DoFollow Links
-
Recommended Images
In the vast expanse of digital architecture, every line of code carries weight.
Some lines create movement, others logic, but together they form the living, breathing systems that define our modern world — from fintech platforms transferring billions in milliseconds to healthcare apps managing patient safety.
Yet beneath every seamless interface and reliable interaction lies an invisible force — functional testing, the unsung craftsmanship that ensures every digital mechanism performs with precision. It is the quality control of the digital age, the silent guardian that transforms human intention into technological integrity.
Functional testing doesn’t just verify software; it validates trust. It ensures that what is designed to happen, does happen — consistently, accurately, and securely. In a world where a single defect can compromise millions of users, functional testing is not a process — it is an ethical commitment to reliability.
This is the story of how confidence is engineered — how functional testing powers the backbone of software integrity.
1. The Quiet Architecture of Assurance
In manufacturing, precision is a measure of trust. A watchmaker calibrates gears with microscopic accuracy; an aerospace engineer checks every bolt against aerodynamic stress models.
In software engineering, functional testing plays the same role. It is the discipline that ensures the mechanisms of logic — loops, inputs, and responses — align perfectly with intended behavior.
Functional testing verifies that the software does what it is supposed to do.
Every function, button, and API call is evaluated against its specification, ensuring that the outcome matches the requirement.
While unit testing inspects individual components, and performance testing measures scalability, functional testing assesses the symphony of function and form — the integrated behavior of systems under real-world conditions.
It answers questions such as:
- Does the checkout button process a transaction correctly?
- Does the API return the right data for every request?
- Do workflows respond consistently across browsers, devices, and environments?
This discipline sits at the core of software quality because integrity is never an accident — it’s an engineered outcome.
2. The Anatomy of Software Integrity
Software integrity is not merely about functionality; it is about dependability.
It’s the assurance that systems behave predictably under every condition — not because of chance, but because of rigorous validation.
Functional testing is the mechanism through which this dependability is continuously proven. It validates three key dimensions of integrity:
- Reliability – Ensuring that the system performs correctly every time, even as it evolves.
- Scalability – Confirming that functionality remains intact as complexity and load increase.
- Compliance – Verifying that software behavior aligns with regulatory and security standards.
In regulated sectors — banking, healthcare, government — this triad of reliability, scalability, and compliance is non-negotiable.
A failed test is not a defect; it’s an early warning against reputational or financial risk.
Thus, functional testing is both shield and mirror — protecting users while reflecting a company’s commitment to excellence.
3. Testing as Craftsmanship: The Engineer’s Signature
Behind every piece of robust software lies the craftsmanship of testing — a discipline often invisible, yet deeply deliberate.
Like a master builder inspecting the foundation of a skyscraper, functional testers validate every joint, every connection, every dependency.
Their tools are scripts, frameworks, and APIs; their artistry lies in anticipating failure before users encounter it.
Functional testing requires both analytical precision and creative intuition.
A tester must think like both a machine and a human — interpreting logic structures while empathizing with user behavior.
This dual mindset defines modern QA excellence:
- Analytical rigor ensures correctness.
- Empathetic design ensures usability.
Together, they shape a testing culture rooted not just in process, but in pride — pride in crafting digital systems that work beautifully because they work correctly.
4. Testing the Distributed World: Complexity Meets Control
In the early days of software, testing was straightforward — applications were monolithic, environments predictable.
But today’s systems are distributed, dynamic, and interconnected, spanning microservices, APIs, and third-party integrations.
This architectural shift has transformed functional testing into a discipline of orchestration.
Testers no longer validate single systems; they validate ecosystems — webs of interdependent modules, services, and external APIs communicating across clouds and continents.
Functional Integrity in Distributed Systems
In distributed architectures, a single function may trigger a cascade of inter-service messages, each dependent on network latency, caching, and security handshakes.
Functional testing must ensure that the entire workflow — from request to response — remains consistent, atomic, and accurate.
For example:
- A payment API in a UK fintech platform may rely on authentication services in Dublin and transaction ledgers in Frankfurt. Functional testing validates that this choreography maintains logical and transactional integrity.
- In a US healthcare application, multiple microservices handle data encryption, patient record retrieval, and audit logging. A functional test ensures these services interoperate flawlessly — without violating HIPAA compliance.
Here, automation frameworks like Postman, Cypress, Selenium, and JUnit act as digital instruments of precision, allowing testers to verify thousands of interdependent functions with repeatable reliability.
In essence, functional testing becomes the conductor of the distributed orchestra, ensuring that even as systems scale, their harmony remains unbroken.
5. Microservices, APIs, and Modular Thinking
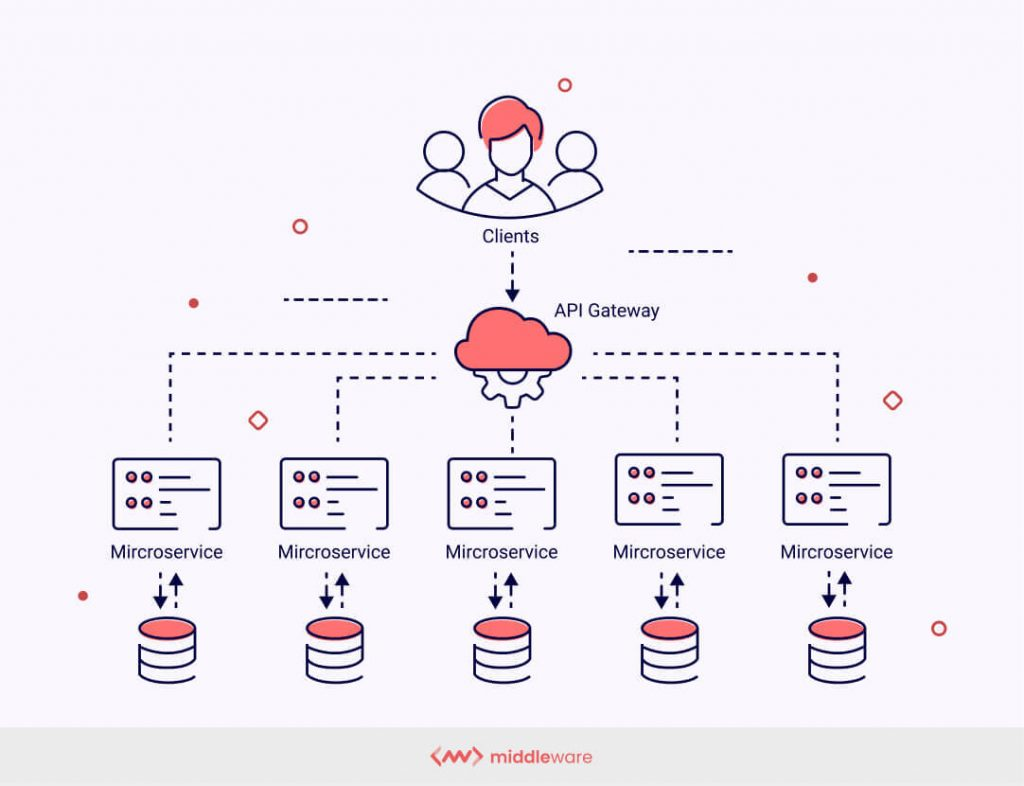
The modern software world thrives on modularity. Microservices and APIs have redefined scalability, enabling agile development, independent deployment, and continuous delivery.
But modularity brings fragmentation — and fragmentation requires functional cohesion.
Testing Microservices
Each microservice must be tested not only in isolation but as part of the greater whole.
Functional tests verify:
- Correct data exchange between services.
- Reliable state management across distributed databases.
- Compatibility across evolving versions.
Testing APIs
APIs are the lifelines of modern digital ecosystems — the invisible handshakes that connect apps, partners, and users.
Functional API testing ensures:
- Input validation (handling malformed or unauthorized requests).
- Output accuracy (consistent response codes and payloads).
- Contract integrity (ensuring updates don’t break dependencies).
For both microservices and APIs, functional testing ensures modular independence without systemic fragility — allowing each component to evolve without breaking the collective structure.
In this way, testing becomes not just validation, but integration design — the craftsmanship of connection.
6. The Discipline of Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Functional integrity doesn’t begin after coding; it begins with coding.
This philosophy underpins Test-Driven Development (TDD) — a methodology where tests are written before the software itself.
In TDD, developers start by defining the expected behavior of a function. The test initially fails (since the function doesn’t yet exist), and only when the code satisfies the test does development move forward.
This approach reverses traditional logic: rather than coding first and testing later, developers engineer toward correctness from the outset.
The TDD Cycle
- Write a test — Define expected behavior.
- Run and fail — Confirm that the test correctly identifies the absence of functionality.
- Write code — Implement logic to make the test pass.
- Refactor — Optimize the code without breaking functionality.
The result is self-validating software — code built with quality embedded into its DNA.
TDD transforms functional testing from a gatekeeper to a co-author of reliable code.
It cultivates a mindset where testing is not overhead, but craftsmanship discipline, much like an architect checking every measurement before construction begins.
7. Automation and Acceleration: Functional Testing at Scale
In large-scale enterprises, software releases are continuous, codebases are massive, and timelines are relentless.
Manual functional testing, while essential for exploration and empathy, cannot sustain this velocity alone.
Enter automation — the engine of modern QA scalability.
Automated functional testing frameworks (such as Selenium, TestNG, Playwright, and Robot Framework) execute repetitive validations at machine speed, ensuring consistency across thousands of builds and deployments.
When integrated into CI/CD pipelines, automation enables:
- Continuous validation after every commit.
- Rapid regression testing.
- Early detection of breaking changes.
The synergy of DevOps and functional testing has birthed a new paradigm: Continuous Quality.
Here, every stage of delivery — from code commit to production release — includes embedded functional validation.
This transforms quality from a final checkpoint into a living, breathing process — constant, adaptive, and intelligent.
8. The Culture of Quality-First Engineering
True software excellence doesn’t arise from tools or processes; it emerges from culture.
A quality-first culture treats testing not as a separate department, but as a shared responsibility. Developers, QA engineers, and product managers collaborate on one mission: software integrity as a collective craft.
In the UK, several government digital teams have adopted this model, embedding QA specialists directly within agile squads — transforming testing from post-production validation into early-stage prevention.
Similarly, in US enterprise environments, QA has become a strategic discipline, influencing design and architecture decisions.
A quality-first culture is built on:
- Transparency: Bugs are opportunities for learning, not blame.
- Empowerment: Testers are not gatekeepers but collaborators.
- Accountability: Everyone owns software behavior, not just functionality.
As a result, organizations move from reactive testing to proactive quality engineering — where confidence is coded, not inspected.
9. Functional Testing and Compliance: Trust Through Verification

In today’s regulatory landscape, compliance isn’t optional — it’s existential.
Functional testing ensures that software not only works, but works within the law.
For instance:
- Financial platforms must comply with PSD2 and FCA guidelines in the UK.
- Healthcare systems must satisfy HIPAA or GDPR requirements for data handling.
- E-commerce and SaaS firms must uphold WCAG standards for accessibility.
Functional tests validate these behaviors through compliance-driven automation — verifying data encryption, privacy workflows, and accessibility checkpoints.
Testing thus becomes a mechanism of digital ethics — proving that integrity extends beyond functionality into moral and regulatory responsibility.
When software passes these tests, it doesn’t just perform; it proves trustworthiness.
10. The Invisible Signature of Excellence
To the untrained eye, a perfectly functioning application looks effortless — seamless interactions, responsive interfaces, consistent outputs.
But beneath that elegance lies the labor of testing: millions of validations, scripts, and iterations, each ensuring that the user’s experience feels simple because it’s built on precision.
Functional testing is the invisible signature of engineering excellence.
Like the watermark on fine architecture, its presence is not seen, but felt — in every bug prevented, every crash avoided, every user retained.
It is what allows businesses to innovate boldly without fearing instability; what allows developers to ship fast without sacrificing correctness; and what allows brands to deliver trust at scale.
When code meets confidence, software becomes more than a product — it becomes a promise kept.
11. Conclusion: Testing as the Heartbeat of Software Integrity
In the grand architecture of digital transformation, functional testing is the foundation stone.
It ensures that innovation remains grounded in reliability, and that every technological leap is matched with ethical assurance.
The future of testing lies not in more scripts, but in smarter validation — powered by automation, AI, and a culture of continuous improvement.
Yet its soul remains unchanged: to ensure that software not only functions, but fulfills its purpose with integrity.
In an age where technology defines trust, functional testing is the quiet craftsmanship behind every digital masterpiece — the invisible assurance that keeps the modern world running, one verified function at a time.