Learn essential cloud application scaling strategies to boost performance, reduce costs, and ensure your application grows efficiently. Discover key benefits, techniques, and best practices.

-
Introduction to Cloud Application Scaling
1.1 What is Cloud Application Scaling?
1.2 Why Scaling is Critical for Modern Businesses -
Types of Cloud Scaling
2.1 Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up)
2.2 Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out)
2.3 Hybrid Approaches -
Key Benefits of Cloud Application Scaling
3.1 Enhanced Performance and Reliability
3.2 Cost Optimization and Resource Efficiency
3.3 Improved User Experience and Satisfaction
3.4 Business Agility and Innovation -
Strategies for Effective Cloud Application Scaling
4.1 Auto-Scaling with Cloud Providers
4.2 Load Balancing and Traffic Distribution
4.3 Containerization and Microservices
4.4 Monitoring and Predictive Scaling -
Challenges and Best Practices
5.1 Common Scaling Pitfalls
5.2 Security Considerations
5.3 Cost Management Tips -
Cloud Scaling in Real-World Applications
6.1 Case Study Examples
6.2 Lessons Learned and Key Takeaways -
Conclusion
7.1 Future of Cloud Application Scaling
7.2 Final Recommendations for Businesses
Introduction to Cloud Application Scaling
In the modern digital era, businesses are increasingly dependent on cloud-based applications to deliver seamless experiences to users across the globe. However, as demand grows and workloads become unpredictable, the need for cloud application scaling becomes critical. Scaling is the process of adjusting computing resources dynamically to maintain performance, availability, and reliability.
Without proper scaling, applications may suffer from latency, downtime, or degraded user experience. Organizations that master cloud scaling not only ensure performance but also gain competitive advantages in cost efficiency, business agility, and customer satisfaction.
What is Cloud Application Scaling?
Cloud application scaling refers to the ability to increase or decrease computing resources based on workload requirements. Unlike traditional on-premise setups, the cloud offers elasticity, enabling businesses to match resources with demand dynamically. This flexibility allows enterprises to handle traffic spikes, optimize costs, and maintain seamless application performance.
Why Scaling is Critical for Modern Businesses
- Unpredictable Workloads: E-commerce platforms, SaaS solutions, and digital services often experience sudden traffic surges.
- Global Reach: Users expect applications to perform reliably regardless of location or device.
- Cost Efficiency: Scaling ensures resources are used only when necessary, reducing wasted infrastructure costs.
- Business Agility: Enables rapid deployment of new features without compromising performance.
Types of Cloud Scaling
Scaling can be approached in different ways, each with unique benefits and use cases.
Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up)
Vertical scaling involves adding more resources to an existing server, such as CPU, RAM, or storage. It’s simple to implement and effective for applications requiring high single-instance performance.
Pros:
- Quick to implement
- Maintains application architecture simplicity
Cons:
- Limited by hardware constraints
- Single point of failure if the instance crashes
Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out)
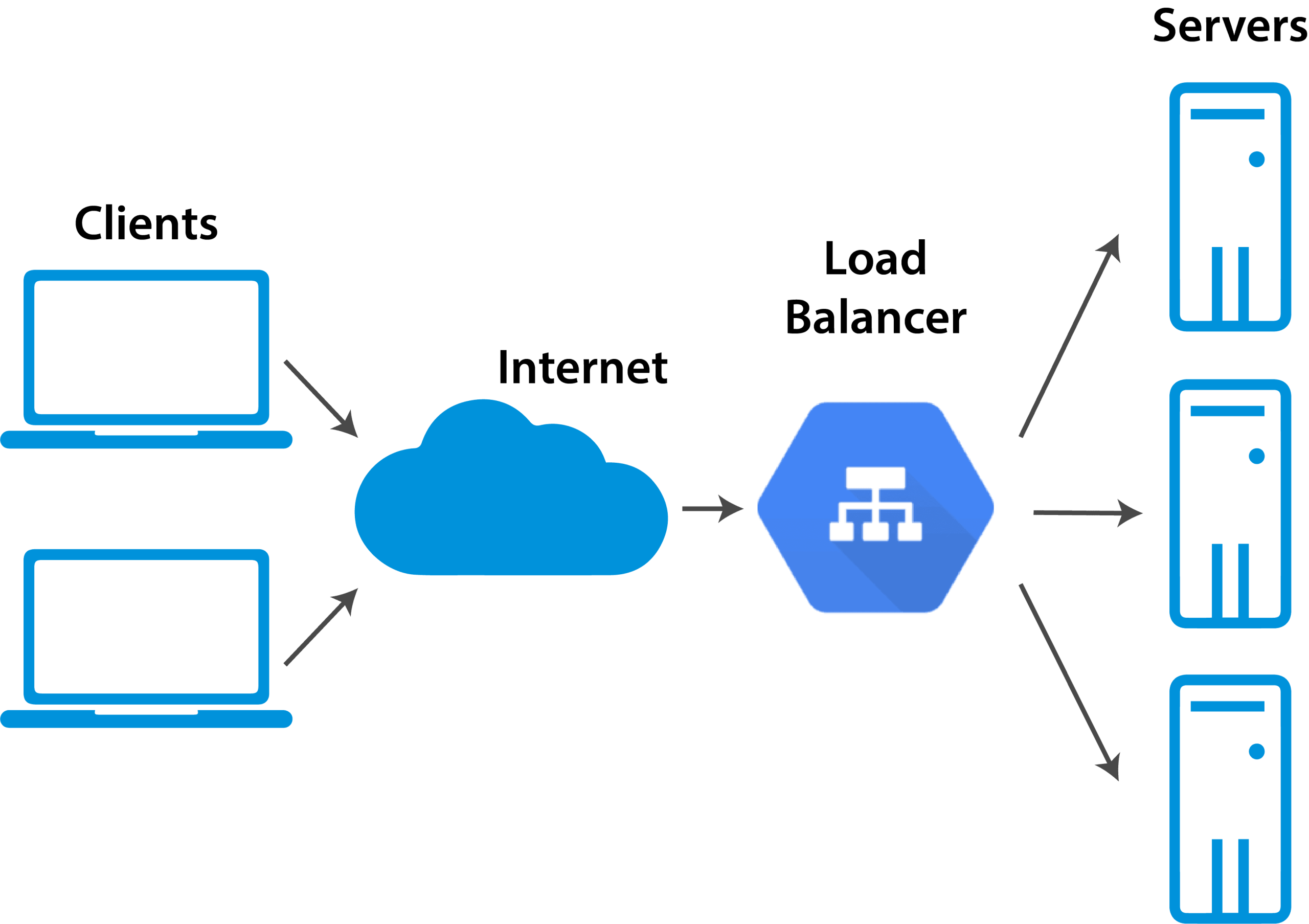
Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers or instances to distribute workloads. This approach is essential for distributed applications and high-traffic platforms.
Pros:
- Better fault tolerance and redundancy
- Handles massive traffic spikes efficiently
Cons:
- Requires distributed system management
- More complex than vertical scaling
Hybrid Approaches
Many enterprises adopt a combination of vertical and horizontal scaling to maximize efficiency. For example, scaling up during moderate demand and scaling out during peak traffic ensures optimal performance without unnecessary costs.
Key Benefits of Cloud Application Scaling
Enhanced Performance and Reliability
Scaling ensures that applications remain responsive, even during traffic spikes or high-demand periods. Users experience faster load times, minimal latency, and uninterrupted services, enhancing overall satisfaction.
Cost Optimization and Resource Efficiency
Dynamic scaling allows businesses to pay only for resources they use, avoiding overprovisioning and reducing cloud infrastructure costs.
Improved User Experience and Satisfaction
Users expect seamless experiences. Scaled applications maintain high availability, fast response times, and reliability, fostering customer loyalty and trust.
Business Agility and Innovation
Scalable cloud applications allow development teams to deploy new features rapidly, experiment with new solutions, and pivot strategies without being constrained by infrastructure limitations.
Strategies for Effective Cloud Scaling
Auto-Scaling with Cloud Providers
Leading cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer auto-scaling services that monitor application metrics and dynamically adjust resources. Auto-scaling ensures resources are added during demand spikes and reduced during low-traffic periods, optimizing performance and costs.
Load Balancing and Traffic Distribution
Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, preventing bottlenecks and improving fault tolerance. Effective load balancing is crucial for high-availability applications and ensures even resource utilization.
Containerization and Microservices
Containers and microservices allow applications to be modular and independently scalable. With platforms like Kubernetes and Docker, businesses can scale specific services without affecting the entire application.
Monitoring and Predictive Scaling
Real-time monitoring of system metrics such as CPU usage, memory, network traffic, and request rates enables predictive scaling. By anticipating traffic patterns, businesses can allocate resources proactively, avoiding downtime and performance issues.
Challenges and Best Practices
Common Scaling Pitfalls
- Overprovisioning or underprovisioning resources
- Ignoring application bottlenecks during scaling
- Lack of monitoring and alert systems
Security Considerations
Scaling should not compromise security. Implementing network segmentation, secure authentication, and access controls ensures that increased resources do not introduce vulnerabilities.
Cost Management Tips
- Monitor cloud usage continuously
- Use reserved instances for predictable workloads
- Implement automated shutdown for idle resources
Cloud Scaling in Real-World Applications

Case Study Example 1: E-Commerce Platform
An online retailer experienced 5x traffic during Black Friday. Using horizontal scaling and auto-scaling policies, the platform handled millions of requests without downtime, maintaining user experience and maximizing revenue.
Case Study Example 2: SaaS Platform
A SaaS company adopted microservices and containerized architecture, enabling individual services to scale independently. During peak usage, critical services received additional resources automatically, preventing latency and improving customer satisfaction.
Lessons Learned and Key Takeaways
- Proper architecture and monitoring are critical for effective scaling.
- Dynamic scaling reduces costs while improving reliability.
- Predictive analytics can prevent performance bottlenecks before they impact users.
Conclusion
Cloud application scaling is not just a technical requirement; it is a strategic business imperative. Scalable applications deliver superior performance, reduce operational costs, and enable business agility. By combining auto-scaling, load balancing, containerization, and proactive monitoring, organizations can handle unpredictable workloads efficiently while maximizing ROI.
At HexaMileSoft, we help businesses design and implement scalable cloud solutions that ensure performance, reliability, and growth. Choosing the right scaling strategy today sets the foundation for future-ready, resilient applications that delight users and drive business success.